^ Pharmacodynamics
Treatment with glucocorticoids, including budesonide capsules (enteric coated) is associated with a suppression of endogenous cortisol concentrations and an impairment of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis function. There was a positive correlation between the percent (%) reduction of AUC 0-24 of plasma cortisol and systemic exposure to budesonide both in pediatric and adult patients.
^ Administration Instructions
^ Patient Counseling Information
Advise Patients to read the FDA-Approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
^ Description
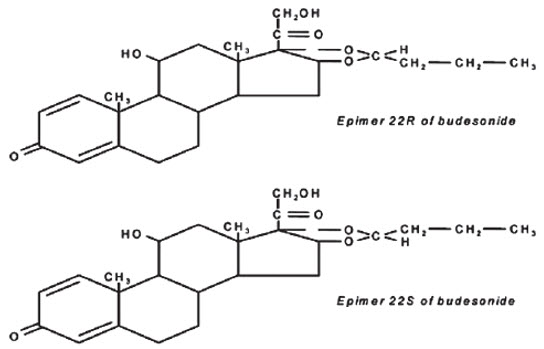
Budesonide, the active ingredient in budesonide extended-release capsules (enteric coated), is a synthetic corticosteroid. Budesonide is designated chemically as (RS)-11β, 16α, 17,21- tetrahydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione cyclic 16,17-acetal with butyraldehyde. Budesonide is provided as a mixture of two epimers (22R and 22S). The empirical formula of budesonide is C 25H 34O 6 and its molecular weight is 430.5. Its structural formula is:
Budesonide is a white to off-white, tasteless, odorless powder that is practically insoluble in water and heptane, sparingly soluble in ethanol, and freely soluble in chloroform. Its partition coefficient between octanol and water at pH 5 is 1.6 × 10 3 ionic strength 0.01.
Budesonide capsules (enteric coated) is formulated as hard gelatin capsules filled with enteric-coated granules that dissolve at pH greater than 5.5. Each capsule for oral administration contains 3 mg of micronized budesonide with the following inactive ingredients: acetyltributyl citrate, ethylcellulose, hypromellose, methacrylic acid copolymer (type C powder), polyethylene glycol, polysorbate 80, sodium lauryl sulfate, sugar spheres (sucrose and corn starch), talc, and triethyl citrate. The capsule shells have the following inactive ingredients gelatin, D&C red #28, D&C red #33, and titanium dioxide. In addition, the black ink S-1-8114/S-1-8115 contains, black iron oxide, D&C yellow #10 aluminum lake, FD&C blue#1 brilliant blue FCF aluminum lake, FD&C blue #2 indigo carmine aluminum lake, FD&C red #40 allura red AC aluminum lake, propylene glycol, and shellac.
^Principal Display Panel - 3 Mg Capsule Bottle Label
NDC 51407-128-01
Budesonide Capsules (Enteric Coated)
3 mg
PHARMACIST: Dispense the accompanying Patient Information leaflet to each patient.
Rx Only 100 Capsules
^ Maintenance Of Clinical Remission Of Mild To Moderate Crohn's Disease
Budesonide capsules (enteric coated) are indicated for the maintenance of clinical remission of mild to moderate Crohn's disease involving the ileum and/or the ascending colon for up to 3 months in adults.
^ Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
^ Symptoms Of Steroid Withdrawal In Patients Transferred From Other Systemic Corticosteroids
Monitor patients who are transferred from corticosteroid treatment with high systemic effects to corticosteroids with lower systemic availability, such as budesonide capsules (enteric coated), since symptoms attributed to withdrawal of steroid therapy, including those of acute adrenal axis suppression or benign intracranial hypertension, may develop. Adrenocortical function monitoring may be required in these patients and the dose of corticosteroid treatment with high systemic effects should be reduced cautiously.
Replacement of systemic corticosteroids with budesonide capsules (enteric coated) may unmask allergies (e.g., rhinitis and eczema), which were previously controlled by the systemic drug.
^ Overdosage
Reports of acute toxicity and/or death following overdosage of glucocorticoids are rare. Treatment consists of immediate gastric lavage or emesis followed by supportive and symptomatic therapy.
If corticosteroids are used at excessive doses for prolonged periods, systemic corticosteroid effects such as hypercorticism and adrenal axis suppression may occur. For chronic overdosage in the face of severe disease requiring continuous steroid therapy, the dosage may be reduced temporarily.
Single oral doses of 200 and 400 mg/kg were lethal in female and male mice, respectively. The signs of acute toxicity were decreased motor activity, piloerection and generalized edema.
^ Hepatic Impairment
Patients with moderate to severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class B and C, respectively) could be at an increased risk of hypercorticism and adrenal axis suppression due to an increased systemic exposure to budesonide [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] . Avoid use in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C). Monitor for increased signs and/or symptoms of hypercorticism and consider dosage reduction in patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class B) [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)] . No dosage adjustment is needed in patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A).
^Patient Information
Budesonide (bue-des-oh-nide) extended-release Capsules (Enteric Coated)
Rx Only
Read this Patient Information before you start taking budesonide capsules (enteric coated) and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking with your healthcare provider about your medical condition or your treatment.
What are budesonide capsules (enteric coated)?
Budesonide capsules (enteric coated) are a prescription corticosteroid medicine used to treat mild to moderate Crohn's disease that affects part of the small intestine (ileum) and part of the large intestine (ascending colon):
It is not known if budesonide capsules (enteric coated) are safe and effective in children under 8 years of age, or in children 8 to 17 years of age who weigh 55 pounds (25 kg) or less, for the treatment of mild to moderate active Crohn's disease that affects part of the small intestine (ileum) and part of the large intestine (ascending colon).
It is not known if budesonide capsules (enteric coated) is safe and effective in children to help keep symptoms of mild to moderate Crohn's disease that affects part of the small intestine (ileum) and part of the large intestine (ascending colon) from coming back.
Who should not take budesonide capsules (enteric coated)?
Do not take budesonide capsules (enteric coated) if:
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking budesonide capsules (enteric coated)?
Before you take budesonide capsules (enteric coated) tell your healthcare provider if you:
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Budesonide capsules (enteric coated) and other medicines may affect each other causing side effects.
How should I take budesonide capsules (enteric coated)?
What should I avoid while taking budesonide capsules (enteric coated)?
What are the possible side effects of budesonide capsules (enteric coated)?
Budesonide capsules (enteric coated) may cause serious side effects, including:
Tell your healthcare provider about any signs or symptoms of infection during treatment with budesonide capsules (enteric coated), including:
The most common side effects of budesonide capsules (enteric coated) in children 8 to 17 years of age, who weigh more than 55 pounds (25 kg), are similar to the most common side effects in adults.
Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of budesonide capsules (enteric coated). For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. You may also report side effects to Mayne Pharma at 1-844-825-8500.
How should I store budesonide capsules (enteric coated)?
Keep budesonide capsules (enteric coated) and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of budesonide capsules (enteric coated).
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use budesonide capsules (enteric coated) for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give budesonide capsules (enteric coated) to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about budesonide capsules (enteric coated) that is written for health professionals.
What are the ingredients in budesonide capsules (enteric coated)?
Active ingredient: budesonide
Inactive ingredients: acetyltributyl citrate, ethylcellulose, hypromellose, methacrylic acid copolymer (type C powder), polyethylene glycol, polysorbate 80, sodium lauryl sulfate, sugar spheres (sucrose and corn starch), talc, and triethyl citrate. The capsule shell has the following inactive ingredients gelatin, D&C red #28, D&C red #33, and titanium dioxide. In addition, the black ink S-1-8114/S-1-8115 contains, black iron oxide, D&C yellow #10 aluminum lake, FD&C blue#1 brilliant blue FCF aluminum lake, FD&C blue #2 indigo carmine aluminum lake, FD&C red #40 allura red AC aluminum lake, propylene glycol, and shellac.
Distributed by: Mayne Pharma Greenville, NC 27834
For more information contact Mayne Pharma at 1-844-825-8500.
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Rev 10/2019
Marketed by:
GSMS, Inc.
Camarillo, CA 93012 USA
^3 Dosage Forms And Strengths
Budesonide extended-release capsules (enteric coated): 3 mg hard gelatin capsules with a pink opaque cap and white opaque body printed with "m580" on the cap in black ink.
^ Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of budesonide capsules (enteric coated) have been established in pediatric patients 8 to 17 years of age who weigh more than 25 kg for the treatment of mild to moderate active Crohn's disease involving the ileum and/or the ascending colon. Use of budesonide capsules (enteric coated) in this age group is supported by evidence from adequate and well controlled studies of budesonide capsules (enteric coated) in adults, with additional data from 2 clinical studies in 149 pediatric patients treated up to 8 weeks and one pharmacokinetic study in 8 pediatric patients [see Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), and Clinical Studies (14.1)] .
The observed safety profile of budesonide capsules (enteric coated) in pediatric patients is consistent with its known safety profile in adults and no new safety concerns were identified [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] .
Systemic corticosteroids, including budesonide capsules (enteric coated), may cause a reduction of growth velocity in pediatric patients. Pediatric patients with Crohn's disease have a 17% higher mean systemic exposure and cortisol suppression than adults with Crohn's disease [see Warning and Precautions (5.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)] .
The safety and effectiveness of budesonide capsules (enteric coated) have not been established in pediatric patients less than 8 years of age for the treatment of mild to moderate active Crohn's disease involving the ileum and/or the ascending colon.
The safety and effectiveness of budesonide capsules (enteric coated) have not been established in pediatric patients for the maintenance of clinical remission of mild to moderate Crohn's disease. An open-label study to evaluate the safety and tolerability of budesonide capsules (enteric coated) as maintenance treatment in pediatric patients aged 5 to 17 years was conducted, and did not establish the safety and efficacy of maintenance of clinical remission.
^4 Contraindications
Budesonide capsules (enteric coated) are contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to budesonide or any of the ingredients of budesonide capsules (enteric coated). Serious hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis have occurred [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)] .
^ Maintenance Of Clinical Remission Of Mild To Moderate Crohn's Disease
The recommended dosage in adults, following an 8 week course(s) of treatment for active disease and once the patient's symptoms are controlled (CDAI less than 150), is budesonide capsules (enteric coated) 6 mg orally once daily for maintenance of clinical remission up to 3 months. If symptom control is still maintained at 3 months an attempt to taper to complete cessation is recommended. Continued treatment with budesonide capsules (enteric coated) 6 mg for more than 3 months has not been shown to provide substantial clinical benefit.
Patients with mild to moderate active Crohn's disease involving the ileum and/or ascending colon have been switched from oral prednisolone to budesonide capsules (enteric coated) with no reported episodes of adrenal insufficiency. Since prednisolone should not be stopped abruptly, tapering should begin concomitantly with initiating budesonide capsules (enteric coated) treatment.
^ Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been reported during post-approval use of budesonide capsules (enteric coated). Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Immune System Disorders: Anaphylactic reactions
Nervous System Disorders: Benign intracranial hypertension
Psychiatric Disorders: Mood swings
^ Cyp3a4 Inhibitors
Budesonide is a substrate for CYP3A4. Avoid use with CYP3A4 inhibitors. Concomitant oral administration of a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor (ketoconazole) caused an eight-fold increase of the systemic exposure to oral budesonide. Inhibitors of CYP3A4 (e.g. ketoconazole, itraconazole, ritonavir, indinavir, saquinavir, erythromycin, and cyclosporine) can increase systemic budesonide concentrations [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] .
^ How Supplied/storage And Handling
Budesonide extended-release capsules (enteric coated) are size #1 hard gelatin capsules with a pink opaque cap and a white opaque body printed with "m580" on the cap in black ink containing 3 mg of budesonide, USP. Capsules are supplied as follows:
^ Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of budesonide capsules (enteric coated) did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients. Of the 651 patients treated with budesonide capsules (enteric coated) in clinical studies, 17 (3%) were greater than or equal to 65 years of age and none were greater than 74 years of age. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
^ Treatment Of Mild To Moderate Active Crohn's Disease
The recommended dosage of budesonide capsules (enteric coated) is:
^ Treatment Of Mild To Moderate Active Crohn's Disease
Budesonide capsules (enteric coated) are indicated for the treatment of mild to moderate active Crohn's disease involving the ileum and/or the ascending colon in patients 8 years of age and older.
^ Other Corticosteroid Effects
Monitor patients with hypertension, diabetes mellitus, osteoporosis, peptic ulcer, glaucoma or cataracts, or with a family history of diabetes or glaucoma, or with any other condition where corticosteroids may have unwanted effects.
^ Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment Of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies with budesonide were conducted in rats and mice. In a two-year study in Sprague-Dawley rats, budesonide caused a statistically significant increase in the incidence of gliomas in male rats at an oral dose of 50 mcg/kg (approximately 0.05 times the maximum recommended human dose on a body surface area basis). In addition, there were increased incidences of primary hepatocellular tumors in male rats at 25 mcg/kg (approximately 0.023 times the maximum recommended human dose on a body surface area basis) and above. No tumorigenicity was seen in female rats at oral doses up to 50 mcg/kg (approximately 0.05 times the maximum recommended human dose on a body surface area basis). In an additional two-year study in male Sprague-Dawley rats, budesonide caused no gliomas at an oral dose of 50 mcg/kg (approximately 0.05 times the maximum recommended human dose on a body surface area basis). However, it caused a statistically significant increase in the incidence of hepatocellular tumors at an oral dose of 50 mcg/kg (approximately 0.05 times the maximum recommended human dose on a body surface area basis). The concurrent reference corticosteroids (prednisolone and triamcinolone acetonide) showed similar findings. In a 91-week study in mice, budesonide caused no treatment-related carcinogenicity at oral doses up to 200 mcg/kg (approximately 0.1 times the maximum recommended human dose on a body surface area basis).
Budesonide was not genotoxic in the Ames test, the mouse lymphoma cell forward gene mutation (TK+/-) test, the human lymphocyte chromosome aberration test, the Drosophila melanogaster sex-linked recessive lethality test, the rat hepatocyte UDS test and the mouse micronucleus test.
In rats, budesonide had no effect on fertility at subcutaneous doses up to 80 mcg/kg (approximately 0.07 times the maximum recommended human dose on a body surface area basis). However, it caused a decrease in prenatal viability and viability in pups at birth and during lactation, along with a decrease in maternal body-weight gain, at subcutaneous doses of 20 mcg/kg (approximately 0.02 times the maximum recommended human dose on a body surface area basis) and above. No such effects were noted at 5 mcg/kg (approximately 0.005 times the maximum recommended human dose on a body surface area basis).
^ Increased Risk Of Infection
Patients who are on drugs that suppress the immune system are more susceptible to infection than healthy individuals. Chicken pox and measles, for example, can have a more serious or even fatal course in susceptible patients or patients on immunosuppressant doses of corticosteroids. In patients who have not had these diseases, particular care should be taken to avoid exposure.
How the dose, route and duration of corticosteroid administration affect the risk of developing a disseminated infection is not known. The contribution of the underlying disease and/or prior corticosteroid treatment to the risk is also not known. If exposed, therapy with varicella zoster immune globulin (VZIG) or pooled intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), as appropriate, may be indicated. If exposed to measles, prophylaxis with pooled intramuscular immunoglobulin (IG) may be indicated. (See prescribing information for VZIG and IG.) If chicken pox develops, treatment with antiviral agents may be considered.
Corticosteroids should be used with caution, if at all, in patients with active or quiescent tuberculosis infection, untreated fungal, bacterial, systemic viral or parasitic infections, or ocular herpes simplex.
^6 Adverse Reactions
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in labeling:
^ Dosage Adjustment In Adult Patients With Hepatic Impairment
Consider reducing the dosage of budesonide capsules (enteric coated) to 3 mg once daily for adult patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class B). Avoid use in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
^ Hypercorticism And Adrenal Axis Suppression
When corticosteroids are used chronically, systemic effects such as hypercorticism and adrenal axis suppression may occur. Corticosteroids can reduce the response of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis to stress. In situations where patients are subject to surgery or other stress situations, supplementation with a systemic corticosteroid is recommended. Since budesonide capsules (enteric coated) contain a corticosteroid, general warnings concerning corticosteroids should be followed. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2), (5.3), (5.4)].
Pediatric patients with Crohn's disease have a slightly higher systemic exposure of budesonide and increased cortisol suppression than adults with Crohn's disease [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4), Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)] . Patients with moderate to severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class B and C respectively) could be at an increased risk of hypercorticism and adrenal axis suppression due to an increased systemic exposure of oral budesonide. Avoid use in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C). Monitor for increased signs and/or symptoms of hypercorticism and consider reducing the dosage in patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class B) [see Dosage and Administration (2.4), Use in Specific Populations (8.6), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] .
^ References
1. Best WR, Becktel JM, Singleton JW, Kern F: Development of a Crohn's Disease Activity Index, National Cooperative Crohn's Disease Study. Gastroenterology 1976; 70(3): 439-444.
^ Mechanism Of Action
Budesonide is an anti-inflammatory corticosteroid and has a high glucocorticoid effect and a weak mineralocorticoid effect, and the affinity of budesonide to glucocorticoid receptors, which reflects the intrinsic potency of the drug, is about 200-fold that of cortisol and 15-fold that of prednisolone.