^1 Indications And Usage
LIMITED POPULATION: DEFENCATH® is indicated to reduce the incidence of catheter-related bloodstream infections (CRBSI) in adult patients with kidney failure receiving chronic hemodialysis (HD) through a central venous catheter (CVC). This drug is indicated for use in a limited and specific population of patients [see Clinical Studies (14)].
Limitations of Use
The safety and effectiveness of DEFENCATH have not been established for use in populations other than adult patients with kidney failure receiving chronic HD through a CVC.
^ Pharmacodynamics
The pharmacodynamics of DEFENCATH are unknown.
^3 Dosage Forms And Strengths
DEFENCATH CLS is available as a sterile, preservative-free, clear, aqueous-based solution in the following strengths:
^ Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment Of Fertility
Carcinogenesis Carcinogenicity studies in animals have not been conducted with taurolidine or heparin.
Mutagenesis Taurolidine was positive in vitro in an Ames reverse mutation assay and it increased mutation frequency in L5178Y mouse lymphoma cells. However, taurolidine was negative in an in vivo combined micronucleus test and comet assay in rats at the highest dose tested, 600 mg/kg/day administered intravenously.
No studies have been conducted with heparin to determine its mutagenic potential.
Impairment of Fertility Fertility studies have not been conducted with DEFENCATH due to its negligible clinical exposure.
^ Description
DEFENCATH (taurolidine and heparin) CLS contains taurolidine, a thiadiazinane antimicrobial, and heparin sodium, an anti-coagulant.
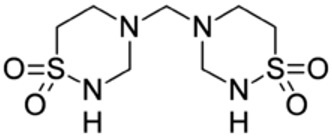
Taurolidine Taurolidine is an antimicrobial agent derived from the naturally occurring amino acid taurine. The chemical name is 4,4'-methylenebis(1,2,4-thiadiazinane)-1,1,1',1'-tetraoxide. The molecular weight is 284.36, and the molecular formula is C7H16N4O4S2.
The structural formula of taurolidine is:
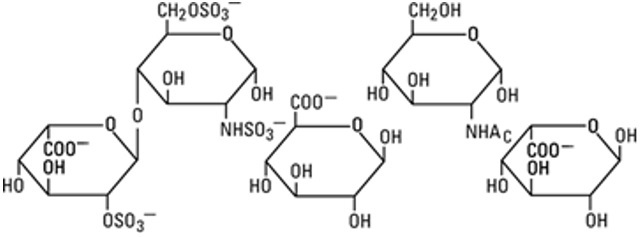
Heparin Sodium Heparin is an anticoagulant consisting of heterogeneous group of straight-chain anionic mucopolysaccharides, called glycosaminoglycans. It is composed of polymers of alternating derivatives of α-D-glucosamido (N-sulfated, O-sulfated, or N-acetylated) and O-sulfated uronic acid (α-L-iduronic acid or β-D-glucuronic acid). Heparin is derived from porcine intestinal mucosa.
The structure of heparin sodium (representative subunits) is:
DEFENCATH is for central venous catheter instillation use. DEFENCATH CLS is available as a sterile, non-pyrogenic, preservative-free, clear, aqueous-based solution of taurolidine and heparin with a pH of 5.5-6.5 in the following strengths:
The heparin potency is determined by a biological assay using a USP reference standard based on units of heparin activity per milligram. The inactive ingredients are 26.1 mg/mL of citric acid, anhydrous (which is added to control pH and maintain the solubility of taurolidine),and may include hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide for pH adjustment.
^ Microbiology
Mechanism of Action The mechanism of action of taurolidine and its metabolites is non-specific, causing damage to microbial cell walls and inhibiting adherence of microorganisms to biological surfaces.
Resistance Time kill studies showed that taurolidine is bactericidal (>3 log10 CFU reduction) at 1x to 4x minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC). The frequency of resistant mutants was <10-9 at 2x and 4x MIC for two strains each of Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Enterococcus faecalis, Enterococcus faecium and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.1
Antimicrobial Activity The following in vitro data are available but their clinical significance is unknown. Taurolidine has been shown to be active against most isolates of the following microorganisms:
Gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus (including methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)) Staphylococcus epidermidis Enterococcus faecalis
Gram-negative Escherichia coli Klebsiella pneumoniae Pseudomonas aeruginosa Serratia marcescens
Fungi Candida albicans Candida glabrata
^ Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Overview of the Safety Evaluation of DEFENCATH
The safety of DEFENCATH was evaluated in a single, active-controlled, double-blind, randomized Phase 3 trial, LOCK-IT-100 (referred to as Trial 1), in adult patients with kidney failure receiving chronic HD through a CVC. In Trial 1, the safety population was comprised of 797 patients with 398 patients using DEFENCATH as a CLS and 399 using heparin as a CLS. Patients used DEFENCATH as a CLS for a mean duration of 173 days, and a range of 4 to 863 days.
The mean age of the patients in Trial 1 was 61 years, 58% of patients identified as male (42% patients identified as female), 63% of patients identified as white and 30% identified as black or African-American. Patients with diabetes at baseline accounted for 70% of patients and the mean body mass index (BMI) of patients in the study was 30. The majority of patients (68%) had been receiving HD for 12 months or less. The location of the CVC was the jugular vein in 92% of patients.
Serious Adverse Reactions and Adverse Reactions Leading to Discontinuation
In Trial 1, serious adverse reactions occurred in 40% (159/398) of patients receiving DEFENCATH as a CLS and 42% (167/399) of patients receiving heparin as a CLS. Adverse reactions leading to death occurred in 5% (18/398) of patients in the DEFENCATH arm and 5% (21/399) of patients in the heparin arm.
Adverse reactions leading to discontinuation of study drug occurred in 17% (69/398) of patients in the DEFENCATH arm and 18% (72/399) of patients in the heparin arm.
Common Adverse Reactions
In Trial 1, adverse reactions were reported in 79% (314/398) of patients using DEFENCATH as a CLS and 79% (315/399) of patients using heparin.
Table 1 lists selected adverse reactions occurring in ≥2% of patients using DEFENCATH or heparin in Trial 1.
Table 2 lists the proportion of patients in Trial 1 that developed loss of catheter patency defined as requiring use of a thrombolytic agent to resolve catheter thrombosis or removal of the catheter due to malfunction/dysfunction.
Other Adverse Reactions
Clinically significant adverse reactions that occurred in fewer than 1% of patients receiving DEFENCATH in Trial 1 are listed below:
Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders: Hypocalcemia
Nervous System Disorders: Dysgeusia
^ Clinical Studies
The efficacy and safety of DEFENCATH for reducing the incidence of CRBSI in patients with kidney failure receiving chronic HD was evaluated in LOCK-IT-100 (referred to as Trial 1, NCT02651428), a randomized, double-blind, active-controlled, multicenter trial.
A total of 806 patients were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive either DEFENCATH or heparin (heparin sodium USP 1,000 units/mL, benzyl alcohol 9.45 mg/mL and sodium chloride 9.0 mg/mL) as a CLS. Enrollment in Trial 1 was not limited to patients with specific types of HD catheters. DEFENCATH or heparin was instilled into central venous HD catheters at the end of all dialysis sessions and was withdrawn prior to the initiation of the next dialysis session. The median age of the study population was 63 years (range 21-94 years); 58% identified as males and 63% identified as white. The majority of patients (98%) had HD treatment three times per week, and 48% had their catheter implanted within three months prior to randomization.
A clinical adjudication committee (CAC) assessed the cases of CRBSI. The CAC definition for CRBSI included one positive blood culture (other than for coagulase-negative staphylococci, which required a confirmatory culture) from a peripheral site or either the arterial or venous catheter hub or the arterial or venous dialysis blood line and the patient had to have signs and symptoms of infection and no other apparent source of bloodstream infection.
Results of analyses of CAC-adjudicated CRBSI among the DEFENCATH and heparin groups in all randomized patients who received at least one dose of allocated study CLS are presented in Table 3. Patients in the DEFENCATH group had a lower incidence of CRBSI events compared to patients in the control group.
In total, 5% [18/397] of subjects in the DEFENCATH arm and 5% [21/398] of subjects in the heparin arm died during the trial (difference [DEFENCATH – Heparin]: -0.7% with a 95% CI[-3.7%, 2.3%]).
Among the 9 patients in the DEFENCATH arm with a CAC-adjudicated CRBSI, 1 had a gram-negative organism isolated and 8 had a gram-positive organism isolated; among the 32 patients in the heparin arm with a CAC-adjudicated CRBSI, 14 had a gram-negative organism isolated and 18 had a gram-positive organism isolated.
^ Heparin-induced Thrombocytopenia
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) was reported at an incidence rate of 0.3% in Trial 1 in patients using heparin, a component of DEFENCATH, as a CLS. If HIT occurs, discontinue DEFENCATH and institute appropriate supportive measures [see Contraindications (4)].
^ Pregnancy
Risk Summary
DEFENCATH is not intended for systemic administration. It is intended for use as a CLS in patients with kidney failure requiring chronic HD; therefore, maternal use is not expected to result in fetal exposure to the drug [see Dosage and Administration (2)]. No animal reproduction study was conducted with DEFENCATH.
^ Drug Hypersensitivity
Drug hypersensitivity reactions were reported at an incidence rate of 0.5% in Trial 1 in patients using heparin, a component of DEFENCATH, as a CLS. If a hypersensitivity reaction occurs, discontinue DEFENCATH and institute appropriate supportive measures [see Contraindications (4)].
^6 Adverse Reactions
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
^ Lactation
Risk Summary
DEFENCATH is not intended for systemic administration. It is intended for use as a CLS in patients with kidney failure requiring chronic HD; therefore, breastfeeding is not expected to result in exposure of the infant to DEFENCATH [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
^2 Dosage And Administration
DEFENCATH is for instillation into CVCs only [see Indications and Usage (1)]. DEFENCATH is not intended for systemic administration. Do not use DEFENCATH as a catheter lock flush product.
Withdraw a sufficient volume of DEFENCATH catheter lock solution (CLS) from the vial using a sterile needle and syringe to fill the catheter lumens. Use 3 mL or 5 mL single-dose vial (depending on the volume of the catheter lumens) to instill DEFENCATH into each catheter lumen at the conclusion of each HD session for patients with kidney failure requiring chronic HD. Prior to initiation of the next HD session, DEFENCATH should be aspirated from the catheter and discarded. If DEFENCATH cannot be aspirated, continue with standard of care CVC preparation and flush with normal saline. If a catheter malfunction is suspected, appropriate standard of care measures should be instituted.
Each DEFENCATH single-dose vial is designed for use with a single patient as a single instillation in the CVC. Discard any unused portion of DEFENCATH remaining in the vial.
^ References
^ Pharmacokinetics
No pharmacokinetic studies were conducted because DEFENCATH is intended to be instilled into the catheter lumens at the conclusion of each HD session for patients with kidney failure requiring chronic HD. DEFENCATH is not intended for systemic administration [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
^ Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of DEFENCATH have not been established in pediatric patients. There are no available data on DEFENCATH use in pediatric patients.
^4 Contraindications
DEFENCATH is contraindicated in patients with:
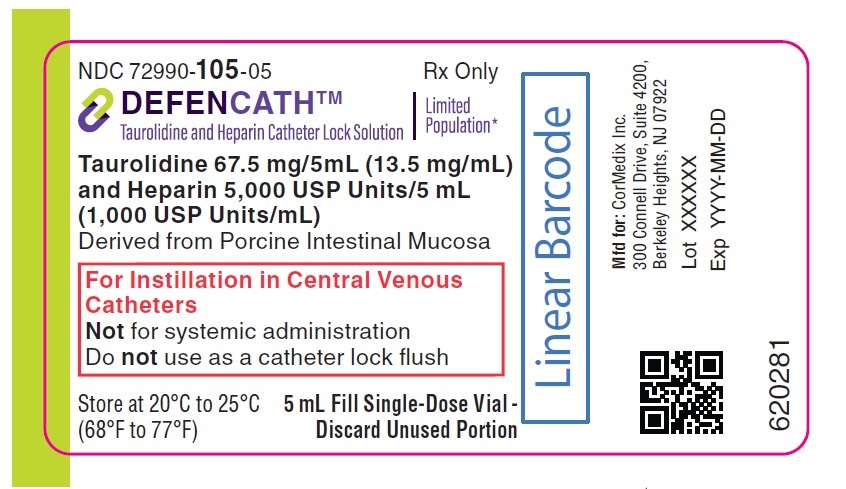
^Principal Display Panel
NDC 72990-105-05
Rx Only
DEFENCATHTM
Taurolidine and Heparin Catheter Lock Solution
LimitedPopulation*
Taurolidine 67.5 mg/5mL (13.5 mg/mL)and Heparin 5,000 USP Units/5 mL(1,000 USP Units/mL)
Derived from Porcine Intestinal Mucosa
For Instillation in Central VenousCatheters Not for systemic administration Do not use as a catheter lock flush
Store at 20°C to 25°C(68°F to 77°F)
5 mL Fill Single-Dose Vial -Discard Unused Portion
^ Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reaction has been identified during the use of a taurolidine and heparin containing CLS outside of the United States. Because this reaction is reported from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate its frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Nervous System Disorders: Paresthesia
^ Mechanism Of Action
Heparin Heparin interacts with the naturally occurring plasma protein, Antithrombin III, to induce a conformational change, which markedly enhances the serine protease activity of Antithrombin III, thereby inhibiting the activated coagulation factors involved in the clotting sequence, particularly Xa and IIa. Small amounts of heparin inhibit Factor Xa, and larger amounts inhibit thrombin (Factor IIa). Heparin also prevents the formation of a stable fibrin clot by inhibiting the activation of the fibrin stabilizing factor. Heparin does not have fibrinolytic activity; therefore, it will not lyse existing clots.
Taurolidine Taurolidine is an antimicrobial drug [see Microbiology (12.4)].
^ How Supplied/storage And Handling
DEFENCATH cathether lock solution is available in:
Each vial contains a sterile, preservative-free, clear aqueous-based solution for instillation in central venous catheters. Each carton contains 10 single-dose vials.
DEFENCATH vials must be stored at a controlled room temperature of 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions are permitted from 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Do not freeze. DEFENCATH vials must be stored in the commercial carton, prior to the instillation in central venous catheters.
Manufactured for:CorMedix Inc. 300 Connell Drive, Suite 4200Berkeley Heights, NJ 07922
^ Geriatric Use
There were 327 patients 65 years of age and older in Trial 1 [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Of the total number of patients using DEFENCATH in this study, 162 (41%) were 65 years of age and older, while 64 (16%) were 75 years of age and older. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between patients 65 years of age and older and younger adult patients.